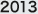
|
* Information contained in this news release is current as of its date of announcement. Be aware that information contained herein is subject to change without notice. |
ICT Used to Promote Voluntary Health Improvement and Disease Prevention in "Visualization of Health Data"
Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project Starts February 2
Aiming to commercializeas majorprogram to support Smart City Project, first starts witha demonstration project
January 31, 2013
Kashiwa City, Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd., e-solutions, inc
Hewlett-Packard Japan, Ltd.,
Medithink
Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project,a demonstration of the “Visualization of Health Data” service using ICT (Information and Communications Technology) will start on February 2 at Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City (Kashiwa-no-ha Campus Area, Kashiwa, Chiba Prefecture.).
The project is being led by a consortium* that includes Kashiwa City, Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd., e-solutions inc, Hewlett-Packard Japan, Ltd., and Medithink.
In the Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project, digital health devices, such as state-of-the-art wristband type life-recorders (activity meters) and body composition monitors with communication functions are linked with a health data analysis system via an ICT network. By using the service, participants can view their own health status through PCs and smart phones. In addition, this service enables the viewing of not only basic health data such as body momentum, calories used and body fat percentage, etc., but also factors such as sleep and other activities, allowing participants to confirm in detail their 24-hour daily rhythms. In this way, participants can easily observe their current health conditions and the cause of any changes in their own conditions.
The aim of the new urban development model for Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City is to achieve a decrease in social security payments by increasing the fitness levels of individuals. The use of the program should encourage voluntary health improvement and disease prevention and so prevent people from getting sick - instead of treating illnesses after people get sick. In order for the new service to become a major program and achieve Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City's aim of “A City of Health and Longevity,” it first has to be trialed by using invited participants as monitors in a one-month demonstration project. For the monitored participants, there is no fee being charged for their participation and required equipment, and by using the service participants can verify the project's benefits in increased health.
Main Characteristics of Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project
- Wristband type life-recorders can be used for 24 hours
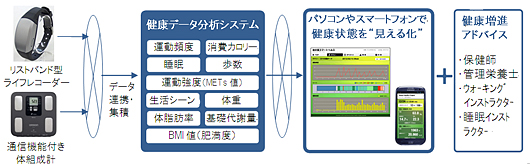
- Can visualize “life-scene analysis” for 24-hour activities, including sleep, a Japan first
- Provides total health care system for managing all health data by linking multiple digital equipment
- Provides various fun functions to encourage continuous use of the service, such as rankings and goal setting
- Provides health guidance and advice from experts, including dieticians and community health nurses
- Creates a health community of users who can exchange health information via dedicated SNS
An overview image of the services of the Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project
- Wristband type life-recorder scan be used for 24 hours
- The device is always attached to the arm, and is the first domestic model of the activity meter that can be worn for 24 hours, even during sleep (from Central Research Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd.: developed but not commercially released; support from Hitachi Systems, Ltd.)
- Continually measures human movement with a 3-axis acceleration sensor, and data is transferred to the system via the network

Wristband type life-recorders
- A Japan first, with visualization of life-scene analysis for 24 hour activities, including sleep
- Data measurement from the axis sensor classified daily activities into 8 types - sleep, rest, desk work, light work, work, walking, jogging and not-wearing the wristband, allowing visualization of an “image” of daily life rhythms
- A total health care system for managing all health data by linking multiple digital equipment
- Uses the gateway server that supports “Continua,” a unified standard for digital health medical equipment; and data linked with body composition monitors from different manufacturers as well as the activity meters
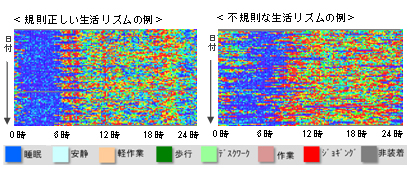
- “Visualization” by accumulating and analyzing a variety of health data, such as exercise frequency, calories burned, exercise intensity (METs value), number of steps, sleep, daily rhythms, body weight, body fat percentage, BMII value (degree of obesity), basal metabolic rate
- In the future, coordinationis plannedwitha wide range of digital health equipment, such as Continua certified blood pressure monitors
- Enables continuous access to the fun items of the service, such as rankings and goal setting
- Ranking display functioncan compare all users for cumulative calories burned
- Target setting function displays graphs of the target values of the number of steps and body weight of each participant
- Provides health guidance and advice from experts, including dieticians and community health nurses
- Community health nurse and dieticians can provide health advice to service users at the beginning of the demonstration with the monitored participants
- Walking instructors and sleep instructors conduct thehealth classes
- Using a dedicated SNS to createa health community of users that can exchange health information with each other
- Based on their data, users can exchange information with each other on how best to sleep and how to exercise in an effective manner
- Supports the health community in their work to address health by assisting participants to find running or sports partners in their local area
- The SNS also provides health advice from experts on walking or sleeping, etc.
Overview of Kashiwa-no-ha Smart Health Project 2012 Demonstration
| Demonstration Period |
February 2 (Saturday), 2013 - March 10 (Sunday), 2013 |
| Details of Demonstration |
- Verification of health benefits in the service of visualization of health data using ICT
- Verification of required functions, the operability of the website and the equipment used
- Verification of local community revitalization when the health SNS is used
- Verification of the commercial needs of the services, its reasonable price, business model and so on
|
| Participation monitors |
Implement using the following monitor targets from the residents of Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City (i.e., residents of the areas surrounding Kashiwa-no-ha Campus Station)
- Use oflife-recorder and human-body composition monitor + participation in health events: 50 persons
- Use of general pedometer + participation in health events: 50 persons
- Use of general pedometer: 50 persons
|
| Equipment Used/Systems |
- Wristband type life-recorders
(from Central Research Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd.: developed but not commercially released; support from Hitachi Systems, Ltd.)
- Human-body composition monitors with communication functions
(OMRON HEALTHCARE Co., Ltd.: HBF-206IT; A&D Company, Limited: UC-411PBT-C)
- Gateway server
(Alive inc.: AP3241 eHealth Gateway Server)
- Health Data Analysis System (newly developed)
- Health Data Visualization Software (newly developed)
|
| Participating Organizations |
- Kashiwa City (implementation of health events/ health consultations)
- Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd. (over all planning and development, project-coordination, and coordination with participating residents)
- Medithink (creationand operation of services/software, construction and commercialization of business model)
- Hewlett-Packard Japan Ltd. (design and development of data analysis system)
- e-solutions, inc. (project management)
|
Note: The project was implemented as part of the “Project to Promote ICT Town Development” contracted by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication with a consortium consisting of the above five parties and AEMC Japan Co., Ltd., International Infomation Network, Street media, Inc., and Ubiquitous Computing Technology Corporation.
|
|
|