Mitsui Fudosan and Tokyo Gas Collaborate in Toyosu Smart Energy Project
Compact Supply of Electricity and Heat to Facilities in Area Around Station, Including Existing Facilities
March 31, 2020
Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd.
Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd.
Tokyo, Japan, March 31, 2020 – Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd., a leading global real estate company headquartered in Tokyo, and Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. announced today that Mitsuifudosan TG Smart Energy Co., Ltd., a company they jointly established, will start the Toyosu Smart Energy Project on Wednesday, April 1, 2020 to provide a stable supply of electricity and heat to the Toyosu 2-chome and 3-chome districts, including to existing facilities. Construction on the Toyosu Energy Center inside Toyosu Bayside Cross Tower was completed on Tuesday, March 31, 2020.
The Toyosu project is the second smart energy project to be operated by Mitsuifudosan TG Smart Energy following the Nihonbashi Smart Energy Project, which started supplying electricity and heat in April 2019.
The Nihonbashi project supplies large-scale independent distributed energy to surrounding areas, including to several existing facilities, thereby successfully improving environmental performance and disaster resilience on a neighborhood-wide level.
The Toyosu project will provide the compact supply of independent distributed energy to core facilities around the station in the Toyosu area, where mixed-use*1 neighborhood creation is under way. The project seeks to create a resilient and environmentally friendly neighborhood.
This energy supply system will cover core facilities where city functions come together, such as areas around stations. Mitsui Fudosan and Tokyo Gas believe that such an energy supply system will serve as a model case for energy solutions that can also be applied to the compact city concept advocated by the Japanese government.
Following on from the projects in Nihonbashi and Toyosu, Mitsui Fudosan and Tokyo Gas will pursue smart energy projects tailored to local characteristics in other areas as well. In the process, information about the creation of resilient and environmentally friendly neighborhoods will be communicated in Japan and overseas.
■Project Overview
- Implement a smart energy project in Toyosu for facilities around the station
- Start supplying independent distributed energy to core facilities located around Toyosu Station: Toyosu Bayside Cross, a large-scale redevelopment, and Toyosu Center Building, which was completed in 1992.
- Improve value added in the Toyosu area, where mixed-use neighborhood creation is under way, by bolstering the disaster preparedness and environmental performance of facilities around the station.
- Energy supply systems for core facilities where city functions come together, such as areas around stations, will serve as a model case for energy solutions for compact cities that are being considered throughout Japan.
- Improve neighborhood disaster preparedness to ensure safe and secure neighborhood creation
- Stably supply energy by using medium-pressure gas pipelines, which are known to have excellent seismic resistance.
- Improve the disaster preparedness of the whole neighborhood by continuously supplying energy to offices as well as temporary accommodation facilities, hotels and other facilities during widespread power outages.
- Help to reduce the environmental impact
- Reduce CO2 emissions by approx. 20% primarily through the effective use of waste heat from CGS*2.
- Analyze big data to project energy demand for the following day and realize optimal operation of facilities based on the projected demand.
- 1 “Mixed-use” means to develop one building, city block or other site for several different uses, such as housing, stores, offices, and cultural facilities.
- 2 CGS stands for cogeneration system. CGS produces electricity and heat from a heat source (city gas) and supplies energy with a high total energy efficiency.
■Project Features
(1) Transforming Toyosu into an even more resilient and environmentally friendly neighborhood through the power of energy
Mitsui Fudosan has adopted the Group Statement, “The Mitsui Fudosan Group aims to bring affluence and comfort to urban living.” Guided by this statement and VISION 2025, the Mitsui Fudosan Group Long-Term Vision, Mitsui Fudosan has been advancing innovative initiatives to establish a sustainable, ultra-smart societies by solving various social problems through the creation of neighborhood. In the Toyosu area, Mitsui Fudosan has been involved in mixed-used neighborhood creation since the 1980s, with a focus on attracting people to the area for various purposes, including not only offices and housing, but also retail, tourism and education. Moreover, Mitsui Fudosan will now strive to strengthen the creation of neighborhood measures that will address neighborhood safety and security, and the environment, with the aim of further enhancing the appeal and value of the Toyosu area and establishing a sustainable, ultra-smart society.
Since its founding, Tokyo Gas has also been working through its business activities to solve social issues such as environmental problems, and to address social priorities such as maintaining and improving a stable supply of energy and energy security. Japan’s Fundamental Plan for National Resilience calls for energy resilience. As part of its efforts to strengthen disaster readiness, Tokyo Gas has prepared a supply network for city gas (gas supplied to homes and businesses in major Japanese cities through underground pipes) that will successfully ensure a stable energy supply even in the event of an earthquake comparable to the Great East Japan Earthquake. In addition, Tokyo Gas has also introduced CGS. It has been involved in initiatives regarding the effective use of energy as a local energy supplier for approximately half a century and aims to realize cities with enhanced energy resilience that are in harmony with the environment. In the Tokyo Gas Group Management Vision Compass 2030, Tokyo Gas has adopted “Enhanced resilience functions through the use of natural gas” as one of its key actions for realizing a sustainable society. Accordingly, Tokyo Gas is striving to expand distributed energy systems in an effort to create disaster-resilient daily lifestyles and neighborhoods where energy can be continuously supplied even during emergencies.
The Toyosu project will attempt to transform the Toyosu area into an environmentally friendly, disaster resilient neighborhood. To do so, Mitsuifudosan TG Smart Energy will set up an Energy Center with a CGS as the main facility and supply locally produced, locally consumed electricity and heat. In this manner, the Toyosu project will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs, which seek to realize a sustainable society by ensuring safe and secure cities and reducing environmental impact.
The Toyosu project is an undertaking that will contribute to progress towards SDGs 7, 9, 11, 12, and 13.

(2) Improving neighborhood disaster preparedness to ensure safe and secure neighborhood creation
The CGS installed as part of the Toyosu project will generate electricity from gas supplied from medium-pressure gas pipelines employing welded steel pipes that have the excellent strength and flexibility needed to withstand land transformation. Medium-pressure gas pipelines are known to have high seismic resistance and have a structure that can fully withstand major earthquakes. Moreover, the gas pipelines have looped supply routes, which ensure high supply stability.
Highly efficient CGS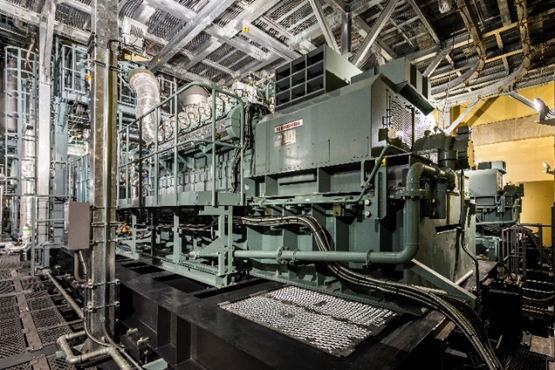
The piping and wiring that will provide the supply of energy was laid anew independently for this project. As a result, a robust network has been built to provide a stable energy supply both in normal times and emergencies.
The Toyosu Energy Center was set up on the above ground floors of a low-story building that offers excellent seismic resistance. Exhaustive measures have been taken to ensure stable operation, allowing the continuous supply of energy even during emergencies. For example, the Toyosu Energy Center’s main facilities were installed on above ground floors, instead of underground, as a measure to mitigate the risk of flooding damage.
With the Toyosu project, the installation of CGS will make it possible to meet the power supply required (50% of peak level) by business continuity plans (BCP) during a widespread power outage. If the water supply is cut off, the supply of heat will be continued by making effective use of water in the heat storage tank as a coolant for heat source facilities. During that time, CGS cooling will be switched to a radiator-based air-cooling process in order to suppress the consumption of valuable water, and the supply of energy will be continued. Urban disaster preparedness will be enhanced by supplying the energy secured in these ways to facilities that will temporarily accommodate those unable to return to their homes during emergencies.
Besides Toyosu Bayside Cross, the project’s energy users will also include Toyosu Center Building, which will soon mark its 30th anniversary. Toyosu Center Building was a flagship project when Toyosu, which had been an industrial shipbuilding area in the past, was transformed into a modern urban neighborhood. Toyosu Center Building will be reborn as a state-of-the-art building with excellent BCP features through energy supply from the Toyosu project.
(3) Helping to reduce environmental impact through the adoption of highly efficient facilities and ICT
The CGS installed as part of the Toyosu project is a model featuring high power generation efficiency made by IHI Power Systems Co., Ltd. Apart from this, highly efficient heat-source facilities have also been installed, and these facilities will help to achieve energy savings. Moreover, CO2 emissions will be reduced by approximately 20% by making effective use of power generation through CGS and waste heat resulting from power generation.
Additionally, an Energy Management System (EMS)*3 utilizing information networks has been built. Energy demand projections will be made for the following day by analyzing big data accumulated on past weather, events and other information. Based on the projected demand, the EMS will enable optimal operation of not only the CGS and self-heating source facilities within the Energy Center, but also the optimal operation of facilities throughout the community, including the heat source facilities of existing facilities. Through this optimal operation, the project will seek to reduce environmental impact.
- 3 EMS stands for Energy Management System. EMS projects an area’s load and through a highly efficient CGS and optimal operation of heat source facility, raises the efficiency rate of waste heat produced by the CGS. This higher efficiency helps to save energy and reduce CO2 emissions throughout the entire neighborhood.
Image of the EMS in the central monitoring room
■Overview of Energy Center
| Date supply starts | April 1, 2020 | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | 5F-8F, Toyosu Bayside Cross Tower, 2-1 Toyosu 2-chome, Koto-ku, Tokyo | |
| Supply area | Parts of the Toyosu 2-chome and 3-chome districts | |
| Floor area supplied | Approx. 0.6 million ft2 (approx. 60,000 m2) | |
| Floor area | Approx. 3.9 million ft2 (approx. 360,000 m2) *Includes space to temporarily accommodate those unable to return home | |
| Planned supply capacity | Electricity: Approx. 14,000 kW Cool heat: Approx. 115 GJ/h Warm heat: Approx. 51 GJ/h |
|
| Main facilities | Gas engines | 2,650 kW × 3 units |
| Waste heat boilers | 1.3 t/h × 3 units | |
| Absorption refrigerating machines with exhaust heat recovery |
1,350 RT × 2 units | |
| Centrifugal chillers | 1,150 RT × 3 units | |
| Steam boilers | 3 t/h × 7 units (single-fuel fired, gas), 2 t/h × 5 units (dual-fuel fired, gas and oil) |
|
Company Overview of Mitsuifudosan TG Smart Energy Co., Ltd.
| Company Name | Mitsuifudosan TG Smart Energy Co., Ltd. |
|---|---|
| Location | Head Office: 1-1, Nihonbashi-Muromachi 2-chome, Chuo-ku, Tokyo |
| Established | March 9, 2016 |
| Capital | ¥100 million |
| Representative | President Kiyoshi Mizumoto |
| Shareholders | Mitsui Fudosan Co., Ltd. (70%) Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. (30%) |


























